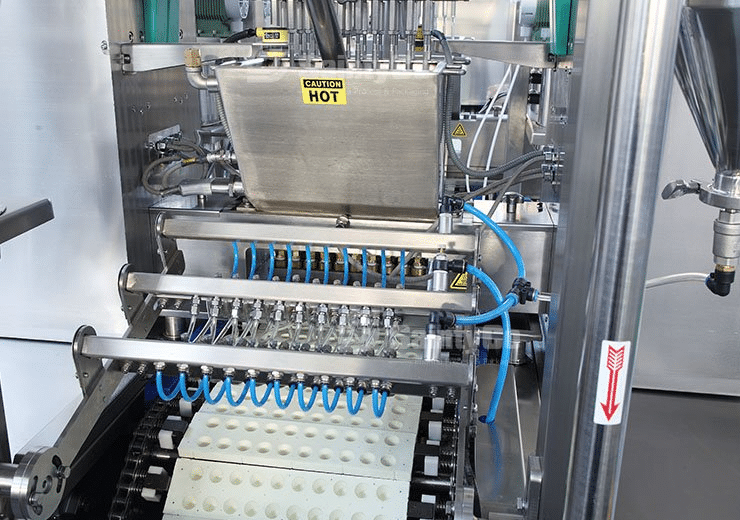
Are you looking to optimize your gummy production operation team?
The ideal number of operators for gummy production varies depending on whether you're using semi-automated or fully automated systems. Typically, a semi-automated gummy production line require 2-3 operators, while fully automated gummy manufacturing setups need 3-5 operators for 2 batches per day for specific tasks like cooking, conveying, coating, monitoring and cleaning.
In this blog, we will break down the roles of these operators, discuss best practices for staffing, and provide insights on how to balance labor with automation effectively.
Semi-automated gummy production requires 2-3 operators.True
This claim is true as semi-automated lines typically function efficiently with 2-3 operators managing the production process.
Fully automated gummy lines need only 2 operators.False
This claim is false; fully automated setups generally require at least 3-4 operators for specific tasks to ensure smooth operations.
How Does Automation Impact Staffing Requirements?
Automation significantly influences staffing requirements, reshaping roles within organizations. Understanding this impact is essential for adapting to evolving workplace dynamics.
Automation reshapes staffing needs by reducing manual roles while increasing demand for specialized positions. It necessitates upskilling existing employees to manage advanced technologies effectively.
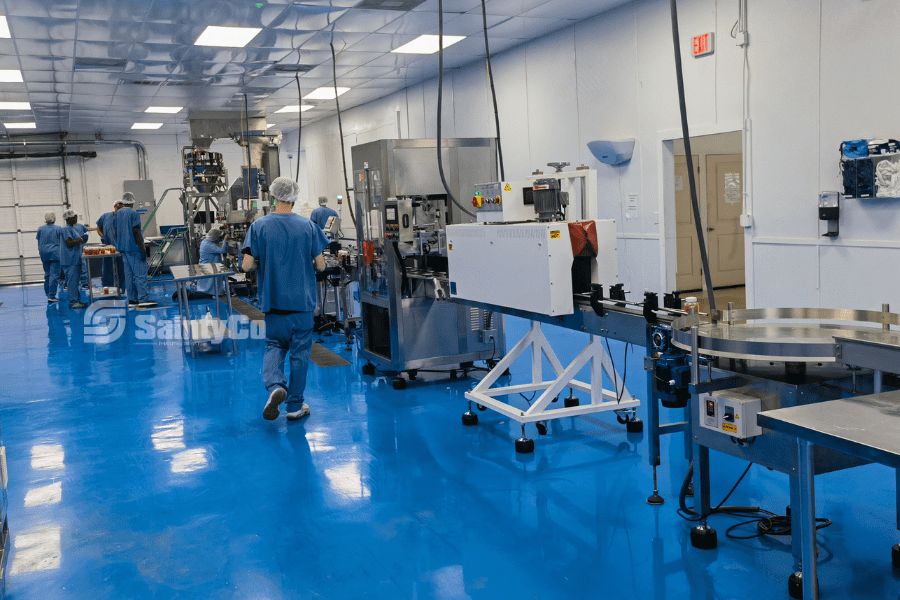
Understanding Staffing Needs in Automated Environments
Automation brings a shift in how staffing needs are evaluated in production environments. With machinery handling repetitive tasks, the human workforce is now focusing on more specialized roles.
For instance, in a semi-automated gummy production line, you may find that only 2-3 operators are required for cooking, depositing, and preparing gummies for drying. This contrasts sharply with fully automated systems, where 3-5 operators are necessary, each assigned specific tasks. This division allows for increased efficiency and productivity.
Job Roles Evolution
Automation doesn't eliminate jobs; it transforms them. Employees are increasingly taking on roles that require monitoring and troubleshooting automated systems. An example can be seen in production efficiency1 metrics that indicate how operators are becoming system managers rather than manual laborers.
Here’s a breakdown of staffing requirements for different automation levels:
| Automation Level | Operators Required | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automated | 2-3 | Preparing,Cooking, Depositing, Demolding,Coating |
| Fully Automated | Only 3 for one batch, 5 for 2 batches a day | Monitoring the whole line, Cooking, Collecting |
As automation increases, the focus shifts towards roles like quality assurance and process optimization.
Addressing Workforce Dynamics
The transition to automation can cause concerns about job security among existing staff. However, it also opens pathways for upskilling and reskilling, ensuring that employees remain valuable in their roles. Training programs can help staff adapt to new technologies and improve their employability in a tech-driven market.
For example, many companies are investing in training initiatives that emphasize technology integration, as highlighted by upskilling strategies2 for their workforce. This not only prepares staff for new roles but also enhances operational efficiency.
Conclusion on Automation's Role in Staffing
In summary, while automation does influence staffing requirements by reducing the number of operators needed for manual tasks, it simultaneously creates a demand for skilled personnel who can oversee these automated processes. It's crucial to understand this dynamic to foster a workforce ready to embrace the future of production.
Understanding the implications of automation on staffing requires careful consideration of both operational efficiency and employee roles. This balance is vital for navigating the changes brought by automation.
Automation reduces the number of manual operators needed.True
As tasks become automated, fewer manual operators are required for production, shifting focus to specialized roles.
Upskilling is essential in automated work environments.True
To adapt to automation, existing employees need training to manage new technologies and specialized tasks effectively.
What Are the Key Roles in a Gummy Production Line?
Understanding the key roles in a gummy production line can help streamline your manufacturing process and improve product quality.
The key roles in a gummy production line include cooking operators, depositing operators, coating specialists, and quality control personnel. Each position plays an essential part in ensuring an efficient and quality-driven production process.

Watch this client video showcasing operators runing a semi-automatic gummy production line with SaintyCo's DM-50X Gummy Depositor in action!
Overview of Gummy Production Roles
In a fully-automated gummy production line, each role is crucial to ensure efficiency and quality.
Cooking Operators
Cooking operators are responsible for mixing ingredients like gelatin, sugar, and flavorings. They follow specific recipes and maintain precise temperatures to achieve the right texture.
Depositing Operators
Once cooked, the mixture is deposited into molds. This task requires operators who can monitor the flow and ensure uniformity in size and shape.
Coating Specialists
After the gummies are formed, they often need a sugar coating. Coating specialists manage this process, ensuring that each gummy is evenly coated for flavor enhancement and appeal.
Manpower Breakdown Example
Here's a breakdown of roles for a fully-automatic gummy production line (SaintyCo G150 Gummy Production Line as an example):
| Role | Number of Operators for 2 Bathes a Day | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Operator | 2 | Prepare and cook gummy mixture |
| Collecting Operator | 1 | Convey demolded gummies to the sugar polishing pan |
| Coating Specialist | 1 | Apply sugar coating to gummies |
| Monitoring Operator | 1 | Oversee the entire production line |
Automation in Gummy Production
With advancements in technology, many production lines are now fully automated. These systems require fewer operators but more specialized roles:
- Control Room Operator: Monitors machinery and adjusts settings as necessary.
- Quality Control Specialist: Conducts checks on the final product to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
To learn more about how automation is reshaping the gummy production process, check out our detailed article on automation benefits3.
Conclusion on Team Collaboration
Each role in the gummy production line must work seamlessly together. Effective communication and collaboration ensure that the final product meets quality standards and customer expectations. For insights on improving team dynamics in production settings, refer to our tips on training an effective teamwork.
Cooking operators ensure precise temperatures during production.True
Cooking operators are crucial for maintaining the right temperatures, which directly impacts the texture of the gummies produced.
Coating specialists are responsible for mixing gummy ingredients.False
Coating specialists focus on applying sugar coatings, not on mixing ingredients, which is the role of cooking operators.
How Can You Optimize Operator Efficiency?
Boosting operator efficiency is crucial for enhancing productivity in manufacturing environments. Here are effective strategies that can lead to substantial improvements.
To optimize operator efficiency, consider integrating technology, enhancing training, streamlining workflows, specializing roles, and fostering collaboration among staff.
Streamline Operations with Technology
Integrating modern technology can drastically improve operator efficiency. For instance, using automated systems reduces manual handling. This means fewer errors and faster production times. Consider investing in software that tracks performance metrics and real-time analytics4. By analyzing this data, managers can identify bottlenecks and make informed adjustments.
Training and Development
Well-trained operators are more productive. Regular training sessions enhance skills and knowledge, enabling staff to handle machinery effectively. Create a structured training program that covers both basic and advanced operational skills. This not only boosts morale but also improves staff retention5. The more skilled your team, the less downtime you’ll face due to operational hiccups.
Optimize Workflows
A clear workflow can significantly enhance efficiency. Map out every step of your production process and identify areas for improvement. Implement lean manufacturing principles to eliminate waste. For example, reducing unnecessary movements or simplifying tasks can save valuable time. A well-defined workflow leads to higher output6 with less effort.
| Task | Current Time | Optimized Time | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooking | 60 minutes | 45 minutes | 25% |
| Depositing | 30 minutes | 20 minutes | 33% |
| Sugar Coating | 40 minutes | 30 minutes | 25% |
Role Specialization
Assigning specific roles to operators can boost productivity. For example, in a fully automated line, designate one person to monitor the entire process while others focus on specific tasks such as cooking or coating. This specialization allows each operator to hone their skills and work more efficiently. Regularly assess roles to ensure they align with operational needs and current demands7.
Foster a Collaborative Environment
Encourage communication among operators to promote teamwork. A collaborative environment allows operators to share insights and troubleshoot issues together. Regular team meetings can facilitate this exchange and help identify areas for improvement. Team cohesion often leads to increased morale8 and a more motivated workforce, which is essential for maintaining high efficiency levels.
Integrating technology reduces manual handling errors.True
Automated systems minimize human error, leading to faster production and improved accuracy in operations.
Regular training sessions decrease operator productivity.False
Well-trained operators enhance their skills, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced downtime during operations.
What Challenges Do Operators Face in Gummy Manufacturing?
Gummy manufacturing presents various challenges for operators. Understanding these obstacles is crucial for optimizing production processes and ensuring high-quality products.
Operators in gummy manufacturing face numerous challenges including equipment reliability issues, temperature control, moisture management, workforce training needs, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Equipment Reliability
Operators in gummy manufacturing often contend with equipment reliability issues. If a machine malfunctions, it can halt production, causing significant delays and waste. Regular maintenance schedules are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Operators must ensure that all machinery, from cooking units to packaging lines, is functioning optimally. For instance, if a depositing machine fails, it can lead to inconsistent gummy shapes or sizes, affecting overall product quality. For more on maintaining manufacturing equipment, check out best practices9.
Temperature Control
Temperature management is vital in gummy production. Gummy mixtures require precise heating and cooling to achieve the desired texture and firmness. Operators face challenges in maintaining consistent temperatures across all stages of production.
For example, if the cooking temperature is too high, it may caramelize the sugars, leading to a burnt taste. Conversely, inadequate cooling can cause gummies to stick together. Understanding the best practices for temperature control can be found in temperature management10.
Moisture Management
Moisture is another critical factor that operators must manage effectively. Excess moisture can lead to gummy spoilage, while insufficient moisture can result in overly hard gummies. This requires careful monitoring of environmental conditions throughout the production process.
To address moisture challenges, operators often utilize dehumidifiers and humidity control systems in their facilities. For insights on moisture control techniques, explore moisture control strategies.
Workforce Challenges
The workforce also presents challenges in gummy manufacturing. As previously noted, semi-automated lines require several operators per shift. Ensuring that all staff members are adequately trained on each piece of equipment is essential for smooth operations.
Additionally, communication issues can arise between team members, especially in high-pressure environments. A structured training program and clear communication protocols can help mitigate these challenges. More information on workforce training can be found in training solutions11.
Regulatory Compliance
Operators must navigate various regulatory standards to ensure product safety and quality. Compliance with FDA regulations and local health codes is non-negotiable in gummy production. This can often lead to operational complexities and potential delays if not managed properly.
Understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial for any gummy manufacturer. For further details on compliance requirements, see regulatory guidelines12.
Summary Table of Operator Challenges
| Challenge | Description | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Reliability | Machine breakdowns causing production delays | Regular maintenance and quick repairs |
| Temperature Control | Maintaining precise temperatures during cooking and cooling | Implementing monitoring systems |
| Moisture Management | Controlling moisture levels to prevent spoilage | Using dehumidifiers and monitoring tools |
| Workforce Challenges | Need for skilled operators and effective communication | Structured training programs and protocols |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to safety and quality regulations | Keeping updated with industry standards |
By addressing these challenges head-on, operators can improve their efficiency and product quality significantly.
Equipment reliability issues can halt gummy production.True
Malfunctions in machinery can lead to significant production delays and waste, highlighting the need for regular maintenance.
Temperature management is unnecessary in gummy manufacturing.False
Precise temperature control is essential for achieving the desired texture and firmness in gummy products, making it a critical factor.
Conclusion
The ideal operator count for gummy production varies: a semi-automated set up need 2-3 operators for tasks such as cooking, depositing, demolding and coating, while a fully automated gummy production lines require 3-4 to ensure efficiency and quality.
At GummyGenix by SaintyCo, we're here to support your journey with cutting-edge, GMP-compliant gummy manufacturing equipment designed for efficiency, precision, and adaptability. Our machines are fully compatible with regulatory standards, and we offer reliable after-sales support to keep your operations running smoothly.
Contact GummyGenix by SaintyCo to explore how our machinery and expertise can enhance your production line. Let’s bring your vision of quality gummy products to life—together.
Gummy Production Machinery from GummyGenix by SaintyCo | Click to Know More
-
Explore this link to gain insights into how automation can streamline your workforce management and improve efficiency. ↩
-
This resource offers strategies for upskilling employees in automated environments, ensuring your team remains competitive. ↩
-
This link provides deeper insights into each role's responsibilities and how they contribute to the overall efficiency of the production line. ↩
-
Discover practical tips to enhance operator efficiency in manufacturing settings. These insights can lead to improved productivity and reduced downtime. ↩
-
Learn about the latest technologies that can improve workflow efficiency for operators in production lines. ↩
-
Explore how specialized training programs can lead to increased operator performance and productivity. ↩
-
Find out how role specialization impacts overall efficiency in manufacturing operations and how to implement it effectively. ↩
-
Understand the benefits of fostering teamwork among operators and how it can enhance overall performance in production environments. ↩
-
Explore detailed insights into gummy manufacturing challenges that can help optimize your production process. ↩
-
Find expert tips on moisture management in gummy production for improved product quality. ↩
-
Learn effective training solutions for your gummy manufacturing workforce to enhance productivity. ↩
-
Stay compliant with regulations in gummy manufacturing by understanding industry standards. ↩